Knowledge work systems and office automation systems serve the information needs at the knowledge level of the organization. , where as office automation systems primary aid data workers (although they are also used extensively by knowledge workers)
Office Automation Systems

Automation allows Institution to update their activities 'in house'. Technical knowledge or web development experience is not necessary. Anyone who can use Microsoft Windows and can browse the internet will have no problem using this system. Entirely database driven, Automation is incredibly robust - making it suitable for sites ranging from low traffic, small business sites to large corporate sites requiring hundreds of updates daily.
One of the key elements in Office Automation is information management. The increasing volume and complexity of business dealings have forced to rely upon computers to help capture, distribute, store, and manage the information flow required in their day-to-day business operations. By having computers keep track of the details of the information, people are able to concentrate on the higher level duties such as planning and decision making.
Automation can help streamline the administration & Research updates. Make a single update within Automation and the piece of content can be updated throughout the sections and reflects in related processes. Automation is accessible via a password protected secure administration area -
with each user being given their own, username & password.
The customizable content within each site is incredibly easy to edit. The system uses an inbuilt modules that enables users to modify data, and image properties via an interface very similar to the one used within "Microsoft Word". More experienced users have the ability to swap to HTML mode for advanced editing.
Data display can be date/time driven, so the information is displayed from, to or in between particular times submitted by you. Submit information when you want, and have it display on the site at a time that suits you.
The ultimate idea is to achieve the goal for CRRI was …
• User Friendly interfaces for data entry and is easy to navigate
• Efficient tracking, monitoring, routing and auditing of various files
• Reliable reporting system that should not affect system performance
• Be easy to maintain and configure
• Be flexible for future enhancements
• Have role/group based security
• Automatic alerts to the user based on events and dead lines
• Fasten decision making process
• Efficient Master data maintenance
• Better control in Inventory Management
• Centralized Controlling System for Authorities
Results
• Paperless Office
o As most of the processes are online, the need of Papers and signature would be
drastically reduced. The system is designed in such a ways that if in any case it is
required to take a approval through papers, it can be generated from the system
and get approved form the concerned officer. This concept will definite save time
and money of the organization.
• Productivity
o Most of the calculation and business logic are intact with the system, so when any
application is sent from a particular officer, the system automatically send the
application to corresponding authority. Also the system gives alert messages when
there is a need t take action immediately. This saves the time of the officers and
also their productivity increases.
• Traceability
o In manual process it is very difficult to trace a particular file and its status. This
system tracks the file movement and the status at each level. This helps the
decision maker to take proper decision in time. Also the application can check
his/her application status any time s/he wants.
• Accountability
o The system makes each and every officer accountable for their job and
responsibility. The reminder message system embedded in the system will send
reminders to the concern officer if s/he is not taking decision in time. Also it make
not of the delay time in making decision/taking action which in turn becomes the
basis of assessing any officer's productivity and decision taking capabilities.
• Interrelated modules
o In the system all the modules share a common data source which helps any officer
to see the related information while taking decision. With single sign-on facility
once can access data from different modules without wondering where to get
proper data.
Knowledge Work System
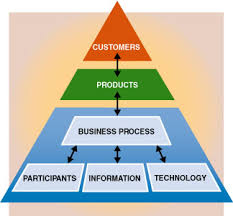
The Knowledge Worker System (KWS) is a computer application designed to help "knowledge workers" (professionals who use information as their primary input and whose major products are distillations of that information) to capture and organize work activity information, and to learn, prioritize, and execute their tasks more efficiently and effectively. KWS integrates methods and technologies from the disciplines of information management, workflow, work scheduling, software agent, and work measurement into a "Performance Support Environment." KWS enhances productivity by delivering task-specific information as needed, and by associating all automated tools, software agents, and multimedia document references needed to complete a specific task.
KWS is "groupware" designed for use by collaborative workgroups. Processes can be assigned across organizations to support matrixed management. Knowledge workers can assign tasks to themselves, to other knowledge workers, or to a group of knowledge workers. KWS improves workgroup coordination by allowing knowledge workers to retrieve and update milestones, task completion, and priority status information.
Read more: http://wiki.answers.com/Q/Office_Automation_Systems#ixzz1GfDyHwEK http://www.erdc.usace.army.mil/pls/erdcpub/www_welcome.navigation_page?tmp_next_page=39811
Read more: http://wiki.answers.com/Q/What_is_an_office_automation_system_and_a_knowledge_work_system#ixzz1GfDV6dDh

